Providing Emergency and Specialty Medicine in Brooklyn, NY
Veterinary Emergency & Referral Group
Who We Are
Who We Are
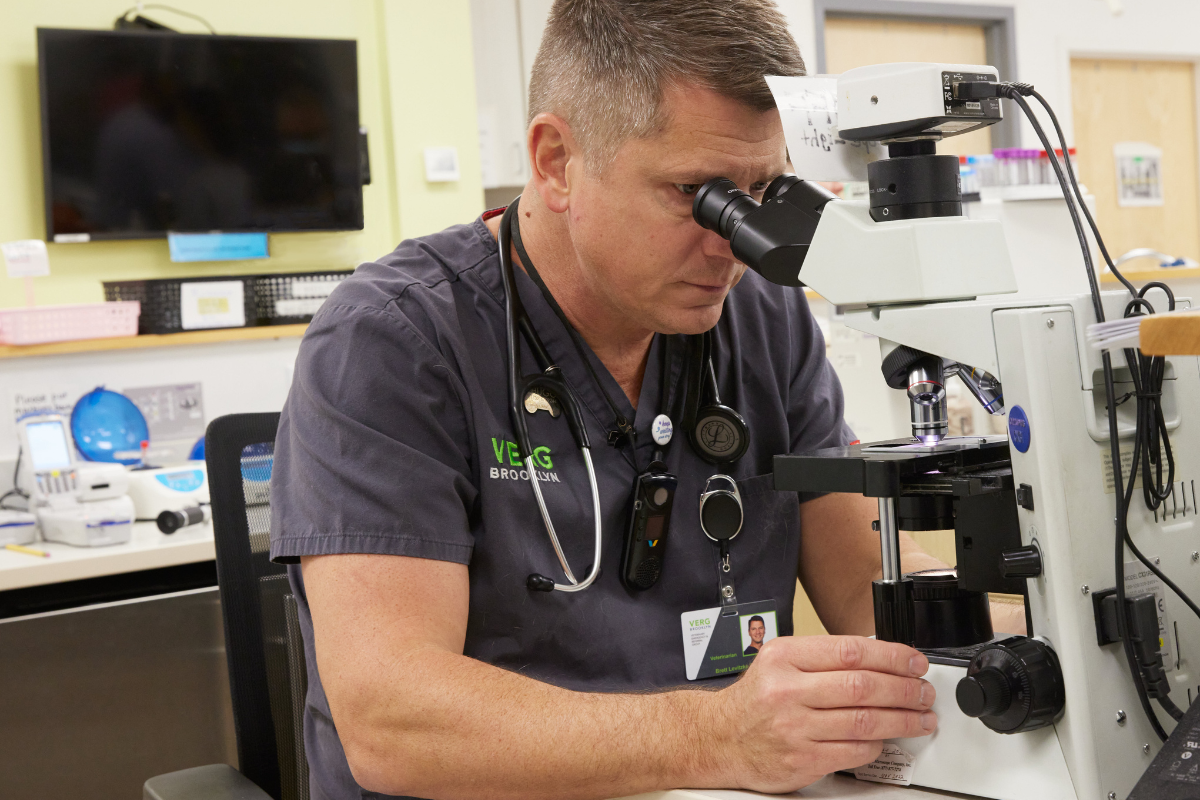
About VERG Brooklyn
Veterinary Emergency and Referral Group (VERG) was formed in 2005 by Dr. Brett Levitzke to provide emergency services and specialty medicine to the tri-state area. Open 24 hours, 7 days a week, our Emergency/Critical Care units consist of teams of experienced and dedicated emergency doctors, technicians, assistants, client service representatives, and financial service representatives working together to provide the highest quality care. . .
Continue reading our mission statement.
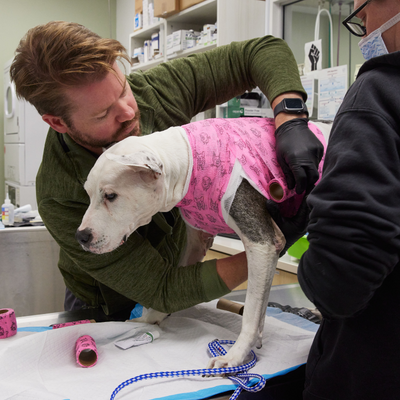
Our Veterinary Services
Emergency & Speciality Veterinary Care in Brooklyn, NY
At VERG Brooklyn, we recognize the value of your pets in your life. With comprehensive veterinary treatment available, our highly qualified staff will treat you and your pets with respect and decency.
Emergency Visits
24-Hour Emergency Care
If your pet is experiencing a medical emergency, please proceed to our facility. To best meet the needs of our community, VERG is open 24-hours a day, 7 days a week.
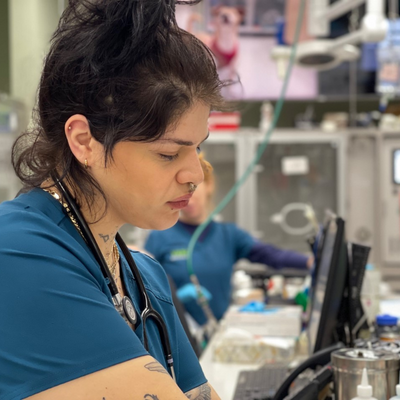
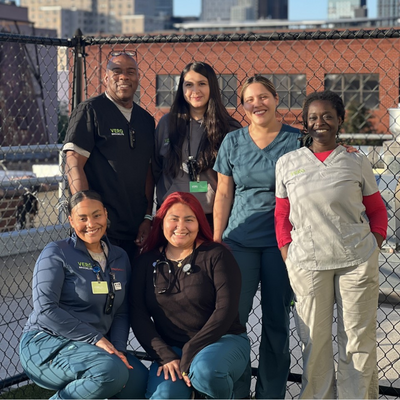
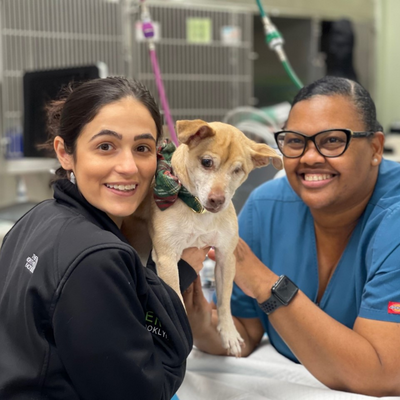
Our Staff
Meet Our VERG Brooklyn Veterinary Team
The veterinary team at VERG Brooklyn is dedicated to your pet’s health and well-being. We deliver high-quality care that meets their ever-changing needs to keep them in good health for years and years to come.
I have had to bring my babies here over the years for various emergencies. I bring them to VERG because I know they will get the best care as quickly as possible. Folks forget that this is an actual ER and wait times depend on how many pets need help. Staff is caring, helpful and straight forward. I wouldn’t go anywhere else.
Our Reviews
Our Reviews
Thank You For Your Kind Words.
Thank you for making VERG Brooklyn one of the highest-rated veterinary hospitals in Brooklyn, NY! Your kind words mean the world to us, and we’re so thankful that you’ve taken the time to provide us with feedback.